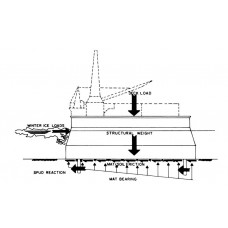
Arctic Marine structures ( سازه های دریایی )
نوع محصول :
قیمت :
-
0تومان
Arctic Marine structures ( مقاله سازه های دریایی )
در این مقاله 40 صفحه ای که به زبان اصلی می باشد از انواع آب و هوا و مناطق دارای صخره یخی تا انواع سازه های دریایی ساحلی و فراساحلی و روش نصب آن ها به صورت اجمالی توضیح داده شده است.
پاراگراف اول این فایل pdf در زیر آورده ایم :
The Arctic Ocean and the adjacent sub-Arctic seas are major challenges for offshore construction. These frontier areas are dominated by perhaps the most severe environmental conditions yet addressed for offshore development. The Canadian and Alaskan Beaufort Sea were the primary areas of interest in the 1980s. In the 1990s the interest has shifted to the east coast of Canada, the Barents and Kara Seas, and offshore Sakhalin. This chapter is largely a synthesis, collecting the construction procedures, data, and guidance that relate to the Arctic Offshore. Some of this material has been previously presented in individual topicoriented chapters. Because of the important role of the Arctic and because work in Arctic regions requires a multidisciplinary approach, it seems appropriate to gather together in one chapter the multiple aspects to which consideration must be given if structures are to be economically and safely built there. Development of the Arctic offshore areas were greatly accelerated by the leasing programs of Canada and the United States in the 1980s. Platforms subject to moving sea ice were constructed in Cook Inlet, Alaska in the 1970s and have given very satisfactory service, although occasionally subject to severe vibration from ice rafts jamming between the legs. Significant but not yet serious loss of underwater plate thickness is reported from the highly abrasive siliceous silts in the constantly moving current. Lighthouses were constructed even earlier in the Baltic Sea, generally of concrete caissons for the substructure with steel or composite steel-concrete towers. A number of failures have occurred due to vibration-induced fatigue of steel shafts, under the cyclic crushing of the ice. Experience from studies of these lighthouses and of icebreaking vessels indicates that the crushing failure tends to become locked in resonance with the natural period of the structure. Abrasion-erosion of the concrete has occurred in these lighthouses in a narrow band from half a meter above to 2 m below sea level. (The tidal range in the Baltic is only about 1 m). Not only has the concrete been eroded but the reinforcing steel has been torn loose. This abrasion problem has occurred only in the narrow neck of the upper Baltic where hard, low-salinity ice has moved past the structure during the spring outflow. Farther north, the hard ice has been largely fast ice; farther south, the ice has been softer, higher salinity ice, so in both these cases, there has been no significant abrasion. The above-water decks of the concrete caisson substructures have also been deteriorated by freeze–thaw attack, especially where salt-water splash has ponded. Corrosion of the reinforcement has occurred to a moderate degree where the freeze–thaw attack and abrasion have removed or reduced the concrete cover. The Russians constructed a prototype tidal power plant at Kislogybusk, 150 km east of Murmansk, in 1970. Although subjected to 4 or 5 months per year of primarily fast ice, there has been no reported damage or deterioration.
برچسب ها: Arctic Marine structures ، انواع سازه های دریایی ، مهندسی سازه های دریایی